A Salicylate is a Salt or Ester of Salicylic Acid. Salicylates are found naturally in some plants (such as white willow bark and wintergreen leaves) and are thought to protect the plant against insect damage and disease. They are widely used across industries, including pharmaceuticals, personal care, food, and industrial applications, for their preservative, anti-inflammatory, and functional properties in various formulations.
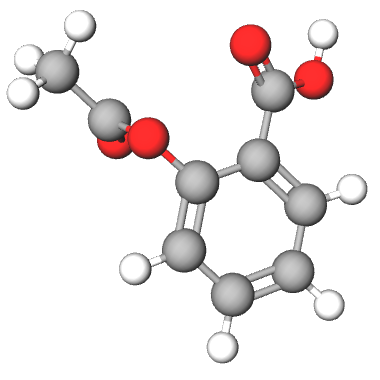
Acetyl Salicylic Acid (Aspirin)
Chemical Name | 2 – Acetoxybenzoic Acid |
Molecular Formula | |
Molecular Weight | 180.2 |
Grades | IP /BP/Ph.EUR /USP-NF |
Description | Colourless / odourless, white crystals / fine crystals / crystalline powder / granules / granular powder |
Packing | 25kg bags |
CAS No. | 50-78-2 |
History Of Aspirin
- Aspirin: A Timeless Remedy with Ancient Roots
- Aspirin, one of the world’s most widely used medicines, has a history that stretches back thousands of years—long before modern chemistry. Its origins trace to the bark of the willow tree, used in ancient civilizations like Egypt and Greece for pain relief and fever reduction. Even Hippocrates, the father of medicine, prescribed willow bark tea to ease pain as early as 400 BC!
- Fast forward to the 19th century, scientists identified salicin, the key active ingredient in willow bark, which led to the creation of Salicylic Acid. While effective, its acidity caused stomach irritation, pushing chemists to refine it further. In 1897, Felix Hoffmann, a chemist at Bayer, successfully synthesized Acetylsalicylic Acid—a gentler, more tolerable version. This became Aspirin, a name that has since become synonymous with pain relief, heart health, and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- From ancient herbal remedies to a modern pharmaceutical powerhouse, Aspirin has stood the test of time—helping millions worldwide while remaining one of the most fascinating success stories in medicine!
Methyl Salicylate
Chemical Name | Methyl 2 – Hydroxybenzoate |
Molecular Formula | |
Molecular Weight | 152.1 |
Grades | IP /BP/Ph.EUR /USP-NF |
Description | Colourless / yellowish / reddish liquid, characteristic odour of wintergreen |
Packing | 35kg / 200kg drums |
CAS No. | 119-36-8 |

Sodium Salicylate
Chemical Name | Sodium 2 – Hydroxybenzoate |
Molecular Formula | |
Molecular Weight | 160.1 |
Grades | IP /BP/Ph.EUR /USP-NF |
Description | White crystalline powder / colourless crystal / shiny flakes |
Packing | 25 kg / 525kg bags |
CAS No. | 54-21-7 |
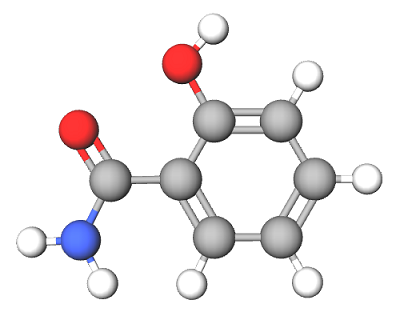
Salicylamide
Chemical Name | 2 – Hydroxybenzamide |
Molecular Formula | |
Molecular Weight | 137.14 |
Grades | USP-NF |
Description | White / odourless crystalline powder |
Packing | 25kg bags / drums |
CAS No. | 65-45-2 |